The Definitive Guide: What is a Cardioid Microphone?
Introduction
Dive into the captivating world of sound recording and audio technology with our definitive guide on cardioid microphones. Perfect for everyone from audio enthusiasts, aspiring musicians, to experienced sound engineers, this guide will shed light on the unique aspects of these popular microphones. If you've ever wondered 'What is a cardioid microphone?' or 'Why is it called so?', then you're in the right place. Read on for an interesting exploration of this subject.
What is a Cardioid Microphone?
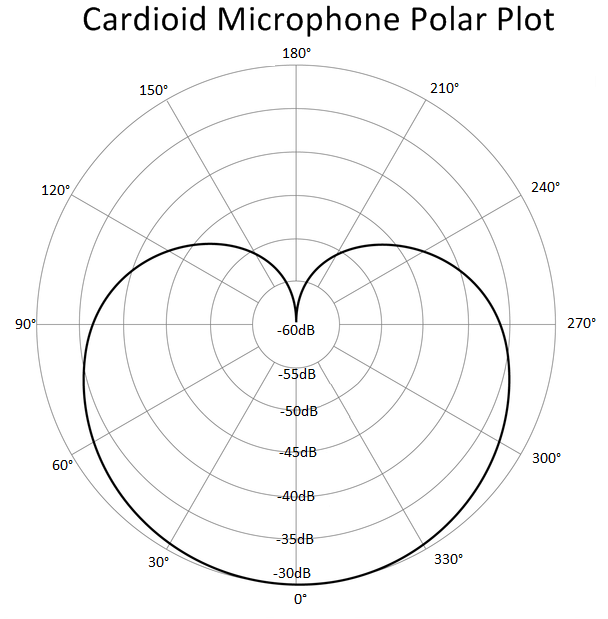
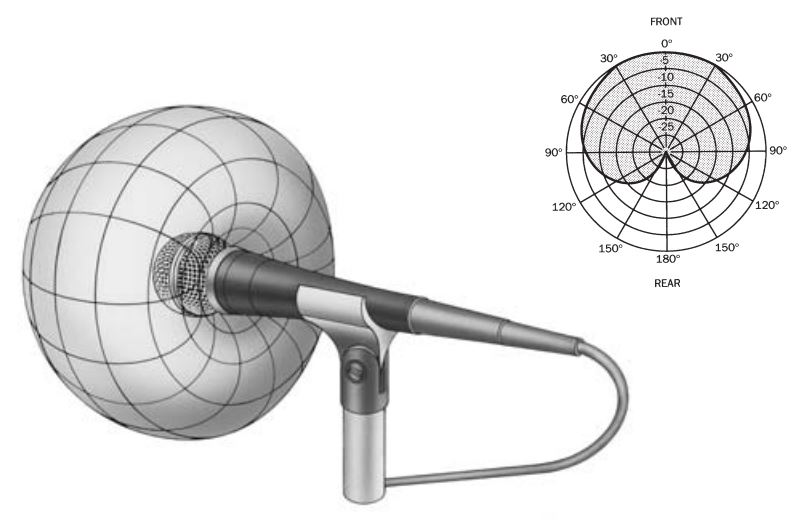
A cardioid microphone is a specific type of directional microphone with intriguing characteristics. It owes its name to the heart-shaped pattern it uses to pick up sound, primarily from the front and sides. This unique pattern is why the term 'cardioid, derived from the Greek word for heart, is fitting for these microphones.
Here’s what you need to know about the cardioid microphone:
- Directionality: The cardioid microphone is front-facing, allowing it to focus on the sound coming directly from in front of it. This makes it perfect for capturing sound in controlled environments such as recording studios.
- Design: This type of microphone is designed to downplay ambient noise. It accomplishes this by minimizing the sound pick-up at the rear, ensuring a clear audio recording from the front.
- Uses: Cardioid microphones are an excellent choice for a variety of situations that require sound recording. These include live performances, studio recordings, podcasts, and broadcasting.
In essence, cardioid microphones offer a user-friendly, effective solution to audio recording by focusing on the source of sound and cancelling out unnecessary background noise. They continue to be a popular choice among sound enthusiasts and professionals worldwide.
Why Are Cardioid Microphones Called So?
Have you ever wondered about the unusual name that cardioid microphones carry? The word 'cardioid' comes from the Greek word 'kardia', which means heart. Here's an in-depth look at the name and how it accurately describes this unique type of microphone:
- Root of the Word: The name was derived from the unique polar pattern that the microphone displays. When visualized on a polar plot, the pattern comes out as a heart shape, leading to the term 'cardioid'.
- Internal Structure: The heart-shaped pattern isn't just a coincidence, but the result of careful design. A cardioid microphone combines the characteristics of a pressure-responsive diaphragm at the front and a pressure gradient responsive capsule at the back. This design facilitates the heart-shaped pattern of sound pick-up.
- Focus of Sound Pick-up: Just like the attention of a human heart is focused on keeping the body running, the 'heart' of a cardioid microphone is centered around picking up sound from the front and minimizing noise from the back. This is why the name cardioid is a perfect description for this microphone type.
- Isolation from Background Noise: Finally, the name 'cardioid' also reflects the microphone’s ability to isolate the main sound source- much like how a heart pumps blood to the most active parts of the body while maintaining lower flow to less active areas.
So, the next time you pick up a cardioid microphone, you'll know that the heart-shaped pattern of sound pick-up and the focus on the sound from the front isn't just an accident – it's what gives the microphone its name and makes it unique.
How do Cardioid Microphones Function?
Cardioid microphones function quite differently as compared to other types of condenser microphones. Their design and working principle revolve around capturing sound from a specific direction while eliminating any sounds coming from the rear. The mechanism behind their operation is indeed incredible and is what gives them the upper hand when it comes to noise cancellation properties. Let's delve deep into how these microphones function:
• Sound Entrances: The microphone has several sound entrances that not only permit sound waves to enter but also combine them in different ways.
• Acoustic Labyrinths: These special pathways within the microphone lead these different sound waves to the back of the microphone's diaphragm.
• Phase Cancellations: As these different sound waves from various entrances meet, they are subject to a series of phase cancellations and reinforcements.
• Negating Sound Waves: Interestingly, the rear of the microphone capsule is designed to negate any sound waves coming from behind. This results in an intentional phase cancellation which contributes to the microphone's unique polar pattern.
• Polar Pattern: The combined effect of all these elements produces the heart-shaped or 'cardioid' polar pattern. This ensures that the microphone picks up more sound from the front and less from the rear.
• Resultant Sound: Through the process of phase cancellation and reinforcement, the cardioid microphone achieves superior sound cancellation properties, enabling it to cancel noises from the sides and rear.
To sum it up, the functioning of cardioid microphones revolves around an intelligent design that amalgamates several sound entrances, acoustic labyrinths, phase cancellations, and reinforcements to ultimately deliver a focused and noise-free sound.
What Sets Cardioid Microphones Apart from Other Microphone Types?
Cardioid microphones carving a unique niche for themselves amidst various microphone types is predominantly due to their unique polar pattern and superior noise exclusion properties. Let's break it down for a more consumable understanding:
• Polar Pattern: Unlike omnidirectional microphones, which indiscriminately pick up sound from all directions, or bidirectional microphones, which capture sounds only from the front and back, cardioid microphones selectively concentrate on the sounds originating from the front. This concentration allows these microphones to capture the nuances of the sound impeccably.
• Noise Cancellation: Besides their intriguing polar pattern, cardioid microphones are notorious for their exceptional sound cancellation qualities. By significantly minimizing ambient noise from the sides and rear, these microphones can deliver a remarkably clearer, focused audio output, even in the midst of a cacophony.
• Application Context: Cardioid microphones effortlessly cater to specific sound recording situations where other types might fall short. Given their intrinsic design, these microphones are most efficaciously used in noisy environments or scenarios requiring the recording of a single sound source amidst multiple ones.
In conclusion, the differentiation of cardioid microphones from other types resides in their ability to deliver a clean, crisp sound recording by concentrating on the intended sound source and efficiently reducing unwanted noise. This unique blend of characteristics makes them a valuable inclusion in any diverse audio-recording setup.
When and Where Are Cardioid Microphones Most Effectively Used?
Cardioid microphones, due to their unique heart-shaped pick-up pattern, stand out for their ability to focus on proximate sound sources while minimising ambient noise. However, their effectiveness greatly depends on the kind of environment or application they're used for. Here's a breakdown of the scenarios where cardioid microphones are most effectively utilized:
1. - Live Performances: Cardioid mics excel in live settings - be it concerts, theatrical shows or presentations - capturing the immediate sound while limiting the capture of audience noise or other onstage sounds.
2. - Podcast Recordings: In the world of podcasting, sound quality is king. The ability of cardioid microphones to isolate speech and minimize intrusive background sounds makes them a popular choice for podcasters.
3. - Broadcasting: For radio or television broadcasting, maintaining the clarity of the presenter’s voice is crucial. Cardioid mics achieve this by effectively rejecting unwanted sounds from the studio environment.
4. - Studio Recording: When recording vocals or solo instruments in a studio, cardioid mics can isolate the intended sound source while eliminating unwanted ambient noises.
5. - Situations Prone to Feedback: Thanks to their front-focused design, cardioid microphones significantly reduce the risk of feedback compared to omnidirectional or bidirectional mics, making them ideal for live sound situations.
In conclusion, the effectiveness of a cardioid microphone relies heavily on its application. Understanding the ideal usage scenarios for these mics can ensure the best audio results and significantly enrich your sound recording experience.
Conclusion
In summary, a cardioid microphone offers a blend of functionality, versatility, and sound quality that sets it apart in the realm of audio recording. Recognizing its unique pattern and understanding when to use it can make a huge difference in your audio projects. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your audio journey, having a cardioid microphone in your toolkit is virtually indispensable.
Related FAQs about what is a cardioid microphone
How does the polar pattern of a cardioid microphone influence sound recording?
The polar pattern of a cardioid microphone directly influences sound recording by focusing on sounds from the front and sides while minimizing noise from the rear. This front-focused pattern enhances sound clarity and reduces unwanted background noise, making it ideal for focused sound recording.
Is there a noticeable difference in quality between a cardioid microphone and an omnidirectional microphone?
Yes, there is a noticeable difference. While both capture high-quality sound, the cardioid microphone excels at isolating the sound source and minimizing background noise. On the other hand, an omnidirectional microphone captures sound from all directions, making it less effective at isolating a single sound source.
In what scenarios would it be less advantageous to use a cardioid microphone?
In scenarios where audio capture from multiple directions is desired, using a cardioid microphone would be less advantageous. This could include capturing ambient sounds or roundtable discussions where equal focus on all sound sources is required.







